Everything about Business Intelligence
Businesses must have a clear view of all their data to remain competitive, which is where Business Intelligence (BI) tools brought in.
Even so, nearly half of all businesses already use BI tools, and projections show that this trend will continue in the coming years.
However, if you haven’t yet adopted a tool or are simply wanting to know more, it may appear difficult to understand BI.
We created this comprehensive guide to provide aspirants on what Business Intelligence is, how it works, and so on.
In this article, we will discuss what Business Intelligence is, how it evolved, how it works, the benefits of BI, examples of BI, creating a BI strategy, categories of BI, pros, and cons of BI, various platforms of BI, Big data and BI, the future scope of BI, and the difference between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics.
Learn more at Softlogic’s Power BI Training in Chennai.
What is BI?
To assist organizations to make more data-driven decisions, Business Intelligence combines business analytics, data mining, data visualization, data tools and infrastructure, and industry standards.
In discipline, modern Business Intelligence is demonstrated when you can obtain a holistic overview of your organization’s data and use that data to drive change, remove inefficiencies, and adapt easily to market or supply changes.
Modern BI solutions prioritize self-service flexibility, administrated data on trusted platforms, equipped business users, and quickness to insight.
It’s worth noting that this is a very modern definition of BI—and BI has a lot of conflicts as a talking point.
Traditional Business Intelligence, complete with capital letters, first appeared in the 1960s as a system for sharing information across organizations.
BI systems progressed, transforming data into insights before becoming highly specialized providing from BI teams with IT-reliant service solutions.
Evolution of BI
“BI is about delivering the correct data to the right audience at the right time so they can make the appropriate decisions,” says Nic Smith of Microsoft BI Solutions Marketing.
The recent evolution of business analytics can be traced back to the introduction of automation in analytics and the concept of big data.
With the advent of big data, analytics and various data sources were expected to become more scalable and powerful.
In the 1980s, Data began to be structured into warehouses and used to access and manage data in a single location.
In the 1990s, BI 1.0 became popular and adoption has grown rapidly since then. However, BI technologies were prohibitively expensive and rigid.
In the 2000s, Real-time data processing emerged to enable appropriate decisions to be made based on current information.
Important BI Milestones
- 1999: IT departments control data, and other departments must request reports.
- 2003: In-memory processing is initiated. – 2004: Tableau 1.0 is released, and it collaborates with QlikView to provide self-service. BI
- 2006: Amazon introduces AWS (Amazon Web Services), ushering in the era of cloud computing.
- 2007: Apple introduces the iPhone, which expands the possibilities for mobile BI. In the same year, IBM acquired Cognos, SAP acquired Business Objects, and Oracle acquired Hyperion for Business Intelligence.
- 2010: Microsoft integrates Power Pivot into Excel, bringing BI to regular business users.
- 2012: Data visualisation techniques are introduced, paving the way for self-service users such as Qlik and Tableau.
- 2015: Microsoft released Power BI, taking the lead in self-service BI tools.
- 2016: Augmented Analytics began to feature BI, aided by machine learning, ushering in a new era of BI.
- 2019: Salesforce acquires Tableau, Sisense acquires Periscope, and Google acquires Looker. AI, ML, and NLP are now being used in conjunction with BI.
- 2020: Low-code or no-code, multi-cloud capabilities, and mobile BI are being used by vendors all over the world.
Major Components of BI
The following are some of the most popular BI components.
- Data Warehouses: It serves as the data source.
- Business Analytics: It aids in the manipulation and mining of data from data warehouses.
- Business Performance Management: It aids in performance monitoring and analysis.
- User Interface: Dashboards are included.
Categories of BI Tools
Business Intelligence has a wide range of tools for providing insights, and some of the most common BI tool types are as follows.
- Spreadsheets: Google Docs and Microsoft Excel are two popular spreadsheet programs that are used as BI tools.
- Reporting Tools: These tools are used to filter, structure, display, and report data. – Data Visualization Tools: These tools are used to transform datasets into easily understandable graphical illustrations, which aids in the acquisition of quick insights.
- Data Mining Tools: These tools aid in the mining of data into recognizable patterns, which can be accomplished through the use of statistics, artificial intelligence techniques, and machine learning processes.
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP): It allows users to analyze datasets based on the business perspectives required.
Applications of BI
There are numerous applications used in Business Intelligence. Here are a few examples:
Ad Hoc Analysis: This is also referred to as ad hoc querying. It is an important feature in modern Business Intelligence applications. Queries are written and executed in ad hoc analysis to analyze specific business-related issues. The analytic results are incorporated into dashboards and reports.
Mobile BI: It aids in the availability of BI applications on mobile devices. These are intended for ease of use and are typically used to view rather than analyze data.
Real-time Business Intelligence (BI): It analyzes data as it is collected, created, and processed. This provides users with an up-to-date view of all areas of interest.
Operational Intelligence (OI): It is a type of real-time analytics that is in charge of providing information to managers and front-line employees. These apps are designed to aid in operational decision-making.
How does BI work?
Businesses and organizations have concerns and targets. To address these concerns and track performance against these targets, they collect the necessary data, analyze it, and make a decision on which actions to take to meet their objectives.
In terms of technology, raw data from business systems has been collected. Before being saved in data warehouses, the cloud, applications, or files, data is processed.
Users can then gain access to the data and begin the analysis process to respond to business challenges. Data visualization tools are also provided by BI platforms, which convert data into charts or graphs and present them to key stakeholders or decision-makers.
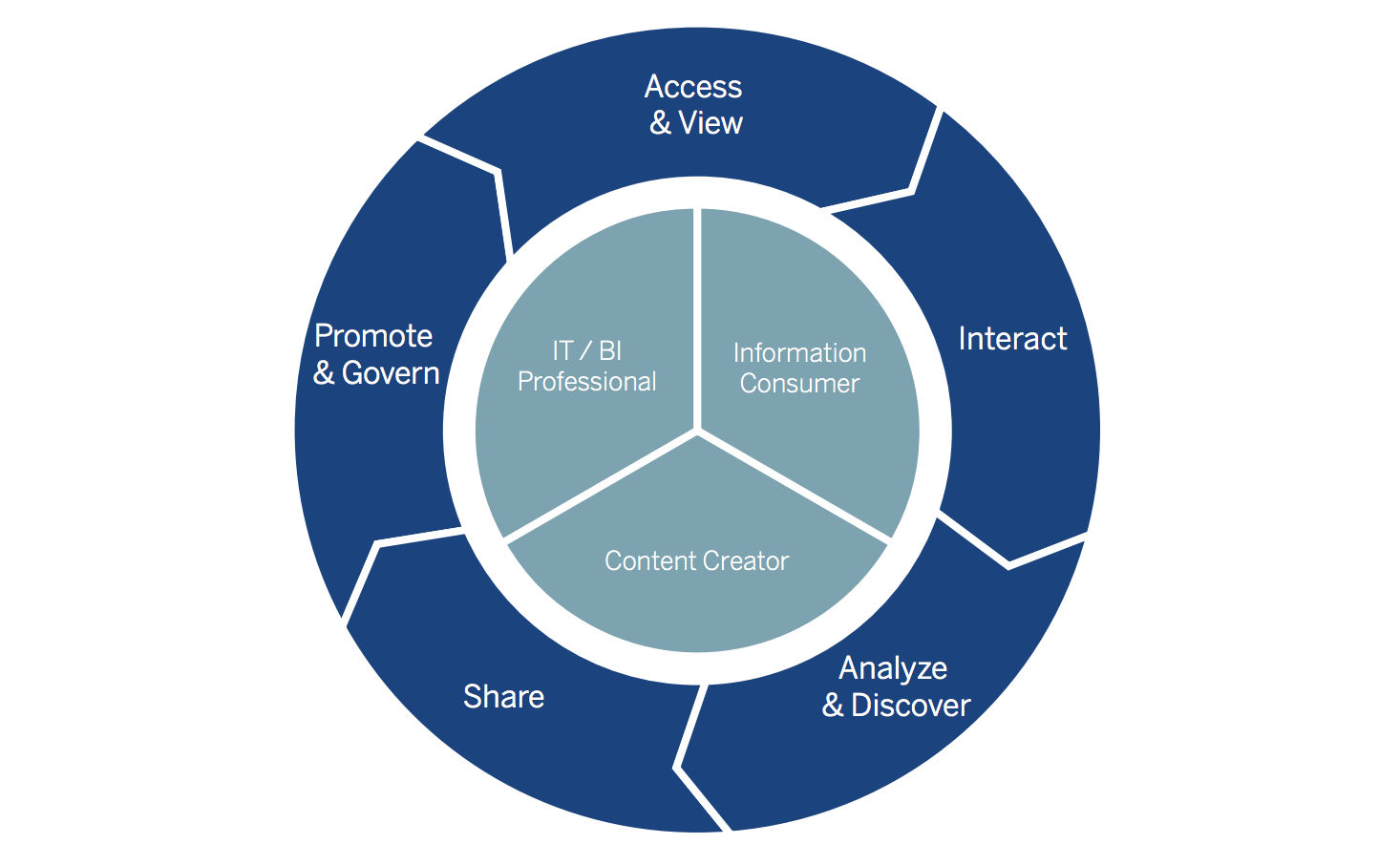
The Architecture of BI is as follows
The BI architecture defines the framework within which all BI technologies are implemented in a company.
This includes IT systems and Business Intelligence tools. The BI architecture is essential in implementing a successful BI program that can use data analysis and reporting to assist a business in tracking performance, optimizing processes, identifying new opportunities, improving planning, and making better decisions.
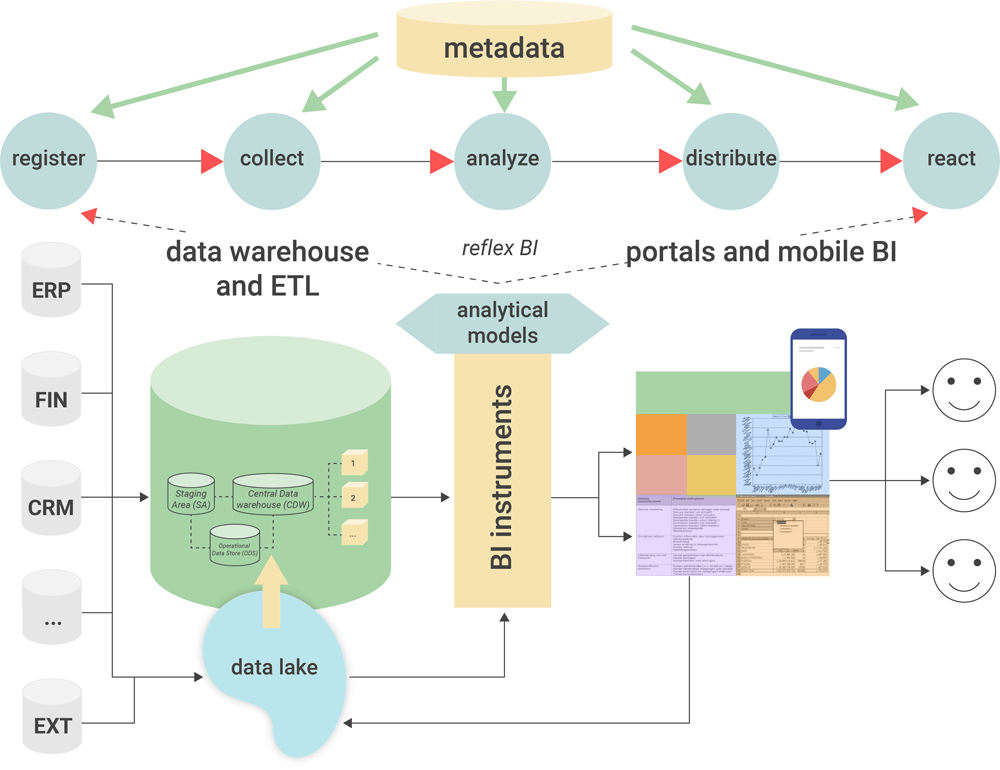
Popular BI Methods
Business Intelligence is a broad term that refers to the processes and methods of collecting, storing, and analyzing data from business operations or activities to improve performance.
All of these factors work together to provide a comprehensive view of a company, allowing people to make more informed, actionable decisions.
Business Intelligence has grown in recent years to include more processes and activities to aid in performance improvement. These are some of the procedures:
Data Mining: It is the process of finding trends in large datasets using databases, statistics, and machine learning (ML).
Reporting: The dissemination of data analysis to stakeholders for them to draw conclusions and make decisions.
Benchmarking and Performance Metrics: Using customized dashboards to compare current performance data to historical data to track performance against goals.
Descriptive Analytics: Exploring what happened using primary data analysis.
Querying: By making data-specific questions, BI gets answers from data sets.
Statistical Analysis: It is about taking descriptive analytics results and making them explore the data with statistics to decide how and why this trend emerged.
Data Visualization: It is the process of transforming data analysis into visual representations such as charts, graphs, and histograms to make data easier to consume.
Visual Analysis: Exploration of data through visual storytelling to communicate insights on the fly and remain in the flow of analysis
Data Preparation: Bringing together multiple data sources, identifying dimensions and measurements, and preparing them for data analysis.
Examples of BI
Let us look at two real-world examples of BI systems.
Example 1
A hotel industry will use Business Intelligence applications to gather data on average tenancy and price per room.
This would aid them in figuring out the total income generated per room. They would additionally be capable of gathering information from all hotels’ market share and customer surveys.
This would assist them in determining their market competitors. If the hotel industry analyses these trends on a monthly and annual basis, they will be able to determine the best discount to offer their customers.
Example 2
The branch manager at a bank could use BI applications to identify the most profitable customers and those who require attention.
Using BI tools also relieves the IT department of a lot of work because they no longer have to create analytical reports. Departments will also have access to more data sources.
Differences between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics
Following are the major differences between BI and Analytics
BI uses available data to analyze the previous patterns for making operations easy. It resolves immediate problems as it is strategic in nature.
It is used for reporting key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics with automated monitoring and alerts.
Business Analytics, on the other hand, analyzes previous trends to make predictive analyses and future forecasts as it is future-focused.
It is tactical in nature and used for statistical and quantitative analysis. It utilizes techniques like data mining and text mining.
Pros and Cons of BI
Implementing BI in business has both advantages and limitations. It is important to note them before implementing them in your businesses.
Advantages of BI
- Improved Data Visibility
- Accurate Reports
- Streamlined Processes
- Boosts Productivity
- Fixed Accountability
- Provides Bird’s Eye View
- Enable Easy Analytics
Limitations of BI
- Initial Cost
- User Resistance
- Data Skill Gap
Tips to choose BI Platforms
To implement BI successfully in your business is to select the appropriate platform based on the tasks.
In choosing your tool, it’s important to keep in mind that what are the key features that will be most helpful for your business. Some of the key features of BI tools are as follows:
- Simple to use
- Tremendous dashboard and visualization options
- Intelligent Insights
- Alerts for good and bad metrics
- In-built artificial intelligence (AI)
- Deployment adaptability
- Compatibility with other platforms and applications
- Data connectivity
- Integration into business applications
Big Data and BI
As the data environment evolves and data collection, storage, and analysis become more complex, it is critical to consider the relationship between BI and big data.
Big data has recently become a buzzword in the industry, so what exactly is it? According to data experts, it is defined by “the four Vs”: volume, velocity, value, and variety.
These four characteristics define and distinguish big data. People typically point to volume as the main defining factor, as the amount of data is ever-increasing and relatively easy to store for long periods.
Future Scope of BI
Because Business Intelligence is constantly evolving to keep up with business needs and technology, we identify current trends each year to keep users up to date on innovations.
Remember that AI and ML will continue to evolve and they lead businesses to incorporate AI insights into a larger BI strategy.
BI efforts to share and collaborate on data will grow exponentially, as businesses aim to evolve more data-driven. It makes Data visualization even more important as teams and departments become centralized.
BI provides near real-time sales tracking capabilities, allowing users to gain insights into customer behavior, forecast profits, and more.
Conclusion
Even if this article covered a lot of fundamental terms of “Business Intelligence“ and its various applications, there is still much more to learn.
We have experts who are constantly growing with their knowledge and staying current with current trends to provide the Best BI Course.
Join in our Data Visualization Training in Chennai for gaining industry-required knowledge to bridge their skill gap.

